Seismic Design Mixed Lateral Systems Which Cs to Use
However for high-performance structures there is now increasing use of dual systems. The equivalent lateral force procedure is a linear static analysis technique that approximates nonlinear building response by use of the response modification factor R which accounts for a buildings inherent ductility and overstrength.
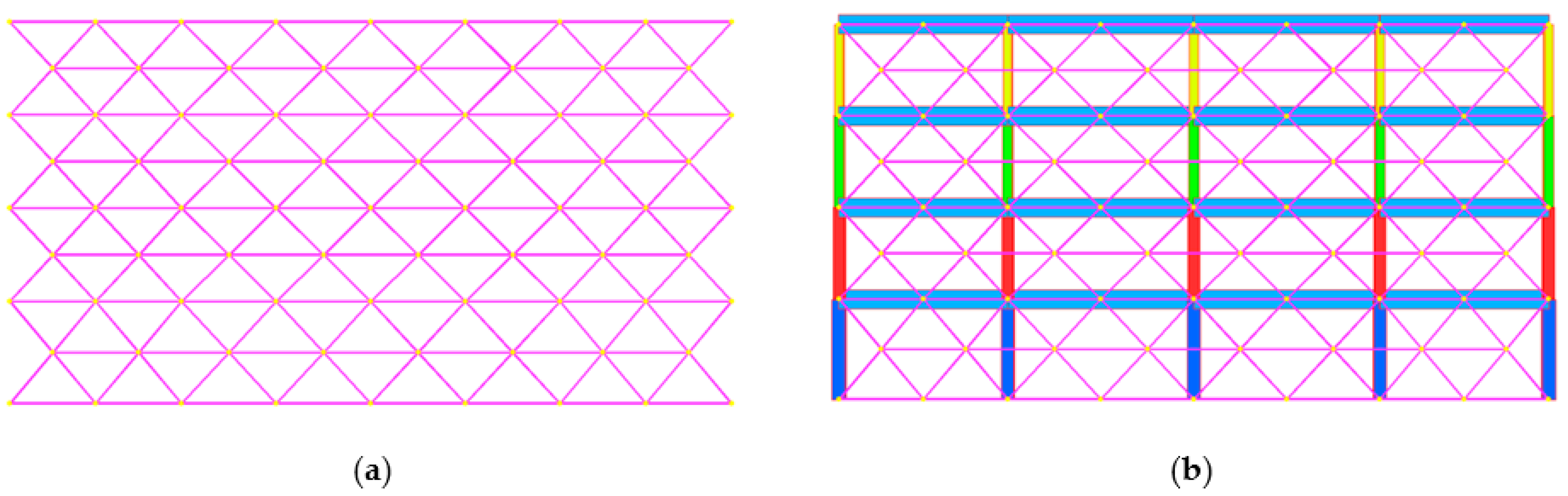
Sustainability Free Full Text Building Retrofitting System Based On Bamboo Steel Hybrid Exoskeleton Structures A Case Study Html
This type of lateral load-resisting system engages a vertical element of the building usually concrete or masonry to transfer the horizontal forces to the ground by a primary shear behavior.

. Designed to hide large openings and blend with adjacent finish options the XLS-2G is a re-engineered system with a modular design and lightweight magnets. It is difficult to obtain what when the 3 lateral resisting systems are mixed. Seismic Design Category A 1141 117 14 14 General Structural Integrity When in Seismic Design Category A you should not use any of the provisions of Chapter 12.
The Importance Factor Ie basically provides for an additional factor of safety of the design loads on the building with values of 100 to 150 used for seismic design more on this in a later article. First the design team must take a multi-hazard. B Detached 1 and 2 family dwellings not included above wood framed less than 2 stories and designed in accordance with the IRC.
Note that the General Structural Integrity provisions have some loads which may often. My answer applies to building in the US. There was no need for complete wind analysis since the seismic design and detailing requirements were more restrictive.
Clearly larger values of the R factor are better given that they reduce the needed resistance to much lower seismic design forces. It is at the strength design level so it may be. Seismic Design Categories.
Wires but not for lateral bracing. ASCE 7 permits the. The values of the R factor contained in the building code range from 1 to 8.
Determine importance factor 8. Accelerations Ss and S are based on historical records and local geology. Instead use the General Structural Integrity provisions of Section 14.
Different seismic-force-resisting systems are permitted along the two orthogonal axes of the structure. Cs is called what. The lateral system should have been designed according to the standards of the jurisdiction in which the building was erected.
See ASCE 7 1253. 25 percent of the design forces. Constructed should be designed to remain stable during the design seismic event because of the potential to contribute to collapse or inadequate performance of the structure should they fail or deform excessively.
Figure 2 shows that the elastic seismic base shear force V e is divided by the R factor to provide the design seismic shear force V s. 12422 requires that a vertical load effect equal to 02 S Ds be applied to dead load. The lateral force resisting system at any story is more than 130 of that for any adjacent story d i d i-1 d i1.
Finally the R factor formally referred to as the Response Modification Coefficient accounts for the ductility of the building and. The new and unique panel attachment design allows for thermal expansion and disengages during a seismic event without impacting surrounding substrates. Shear walls are inherently stiff elements and are therefore extremely effective at resisting lateral wind loads.
1 - Estimate the total. Select structural system and system parameters. In the 1997 UBC the earthquake load E is a function of both the horizontal and vertical components of the ground motion.
Spectral Response Acceleration which is based upon many factors. The total seismic force resistance is to be provided by the combination of the moment frame and the shear walls or braced frames in proportion to their rigidities. Emh 0QE ASCE 7 124-7 where.
C S The Seismic Response Coefficient S DS The short period design spectral response acceleration parameter S D1 The 1 second design spectral response acceleration parameter T The fundamental period of the structure R The Response Modification Factor of the structure this factor is based off of the structural system being used. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451 Design Examples Seismic Load Analysis 9 - 20. The horizontal seismic load effect with overstrength factor Emh shall be determined in accordance with the following.
System Response Factors for Prestressed MasonryIn determining seismic base shear and story drift for structures whose seismic lateral force-resisting system consists of prestressed masonry shear walls the value of the response modification coefficient R and of the deflection amplification factor C d are required to be taken equal to those used for ordinary plain. QE effects of horizontal seismic forces from the seismic base shear V per ASCE 7 1281 or the seismic lateral force Fp per ASCE 7 1331. When designing the primary lateral force resisting system I would have several pages of seismic base shear calculations and oh yeah a one- or two-line calculation of the wind forces just to show that seismic governed.
128-2 is used to determine the seismic response coefficient Cs. Lateral bracing connections must be capable of holding at least 250 lbs. Designed to IBC 1993 to 2012 standards.
Determine seismic design category A-F 7. It is applied as a dead load factor adjustment and may act downward or upward. The diaphragms are rigid as defined in Section 1231 or for diaphragms that are flexible the distance between vertical elements of the seismic force-resisting system does not exceed 40 ft.
This TEK discusses the equivalent lateral force procedure which is the most commonly used technique for seismic analyses. A Detached 1 and 2 family dwellings with a Ss. In order to perform the seismic analysis and design of a struc-ture to be built at a particular location the actual time history record is required.
Lateral loads resisting system may be on or more of the fol-lowing systems. This is the equivalent of the 180 pound 800 N connection force at 45 degrees. Answer 1 of 3.
The 1997 UBC seismic design provisions are based on strength-level design rather than service-level design. Higher R values react better to. This resource page provides an introduction to the concepts and principles of seismic design including strategies for designing earthquake-resistant buildings to ensure the health safety and security of building occupants and assets.
Known as the 02 sec spectral response acceleration Ss subscript s for short period it is used along with the 10 sec spectral response acceleration mapped in a similar manner to establish the loading criteria for seismic design. The structural systems are called lateral load resisting systems. 5222 Combinations of Framing Systems.
This connection force does not apply to the overall design of the lateral. Seismic Design According To 1997 UBC The Static Lateral Force Procedure. 8 Vertical Seismic Load Effect E v.
The essence of successful seismic design is three-fold. Moment resistant frames Braced frame In-. To obtain balanced resistance when they are mixed.
The aerial extent of approach embankment and embankment surrounding cut-and-cover tunnels seismic design and mitigation if. Lath and Plaster ceilings are no longer exempt and will require custom solutions Seismic Design Category.

Ductile Design Of Steel Structures By Pedro Antonio Jimenez Sanchez Issuu
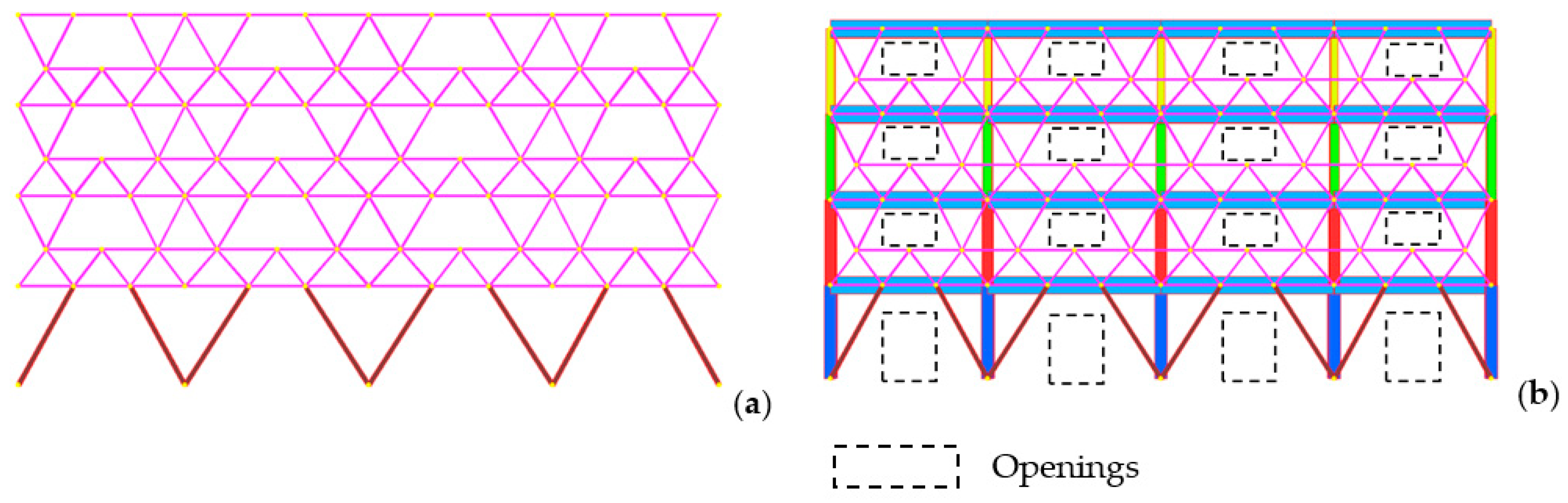
Sustainability Free Full Text Building Retrofitting System Based On Bamboo Steel Hybrid Exoskeleton Structures A Case Study Html
Seismic Lateral Force Resisting System Reinforced Concrete Core Wall Download Scientific Diagram

Seismic Lateral Force Resisting System Reinforced Concrete Core Wall Download Scientific Diagram
Lateral Load Resisting Systems For Multi

Superior Design Solutions Of Section Sizes In Steel Buildings For Different Lateral Frame Systems And Column Shapes Takagi 2020 Japan Architectural Review Wiley Online Library

Superior Design Solutions Of Section Sizes In Steel Buildings For Different Lateral Frame Systems And Column Shapes Takagi 2020 Japan Architectural Review Wiley Online Library
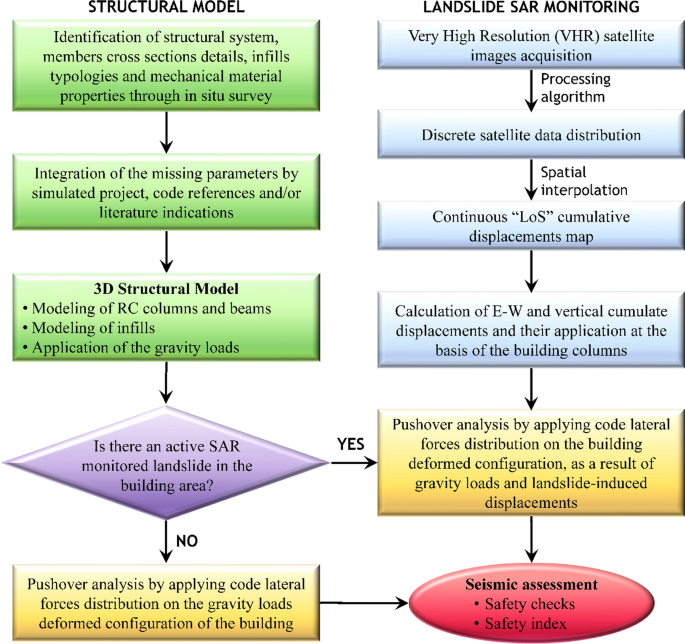
Potential Of Remote Sensing Data To Support The Seismic Safety Assessment Of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Affected By Slow Moving Landslides Springerlink
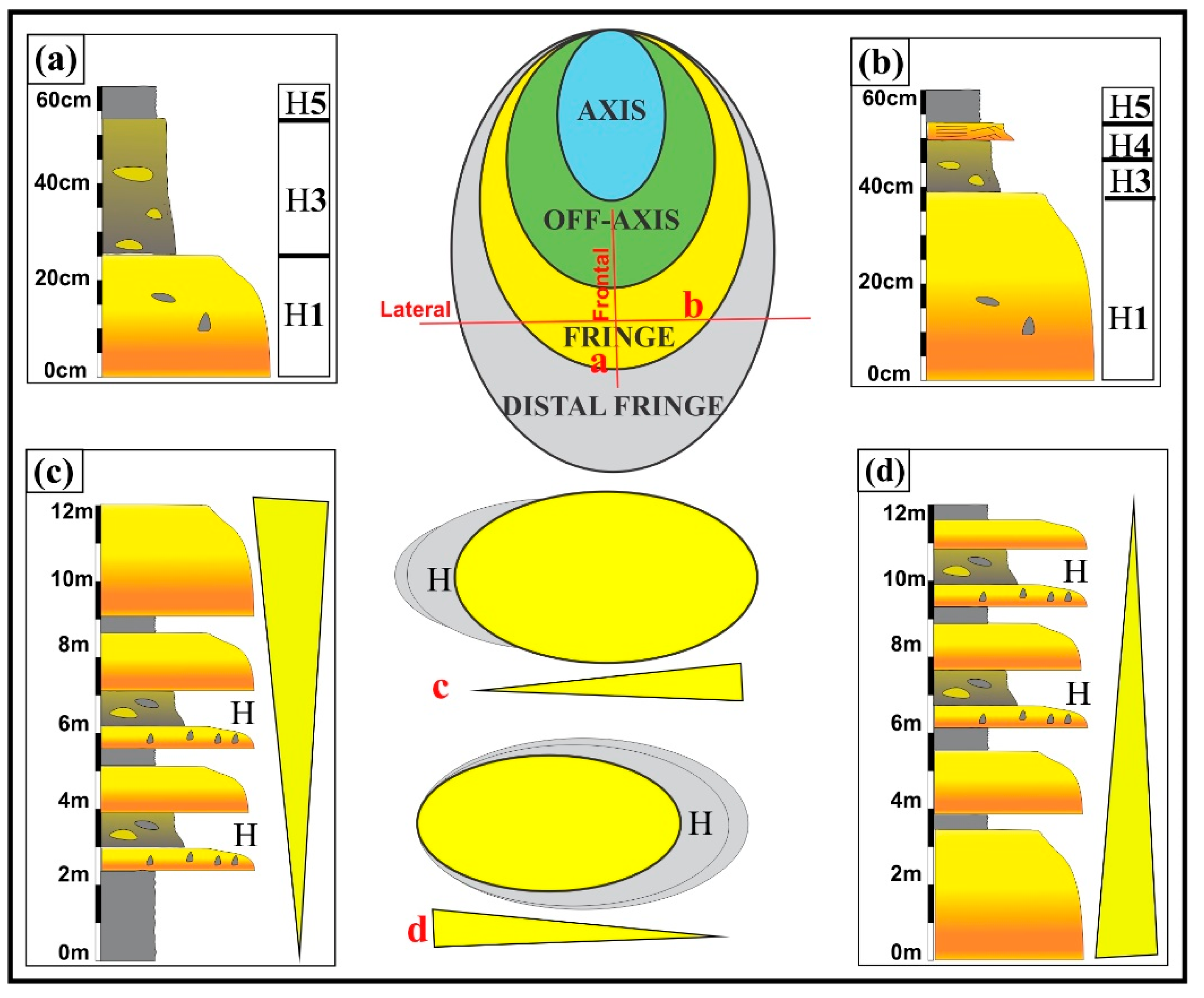
Jmse Free Full Text Facies Analysis And Sedimentary Architecture Of Hybrid Event Beds In Submarine Lobes Insights From The Crocker Fan Nw Borneo Malaysia Html

Pdf Geotechnical Seismic Isolation

Pdf Seismic Design Guide For Low Rise Confined Masonry Buildings

Resilience Based Seismic Design Of Buildings Through Multiobjective Optimization Sciencedirect

Superior Design Solutions Of Section Sizes In Steel Buildings For Different Lateral Frame Systems And Column Shapes Takagi 2020 Japan Architectural Review Wiley Online Library
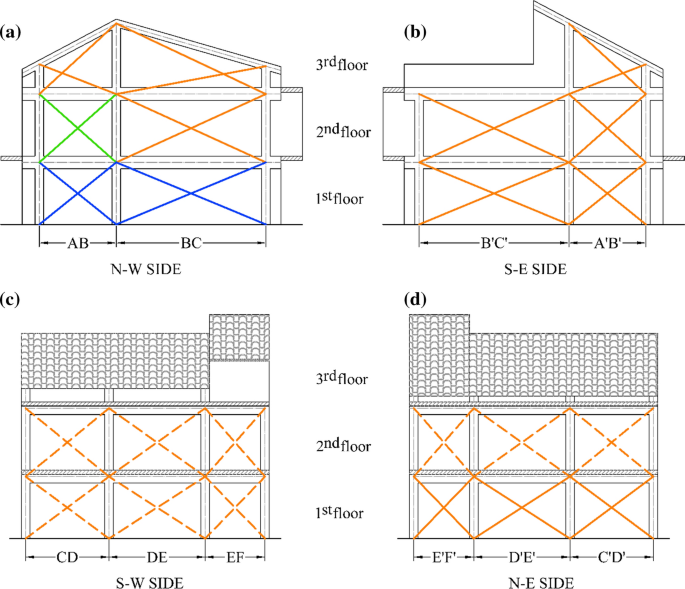
Potential Of Remote Sensing Data To Support The Seismic Safety Assessment Of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Affected By Slow Moving Landslides Springerlink
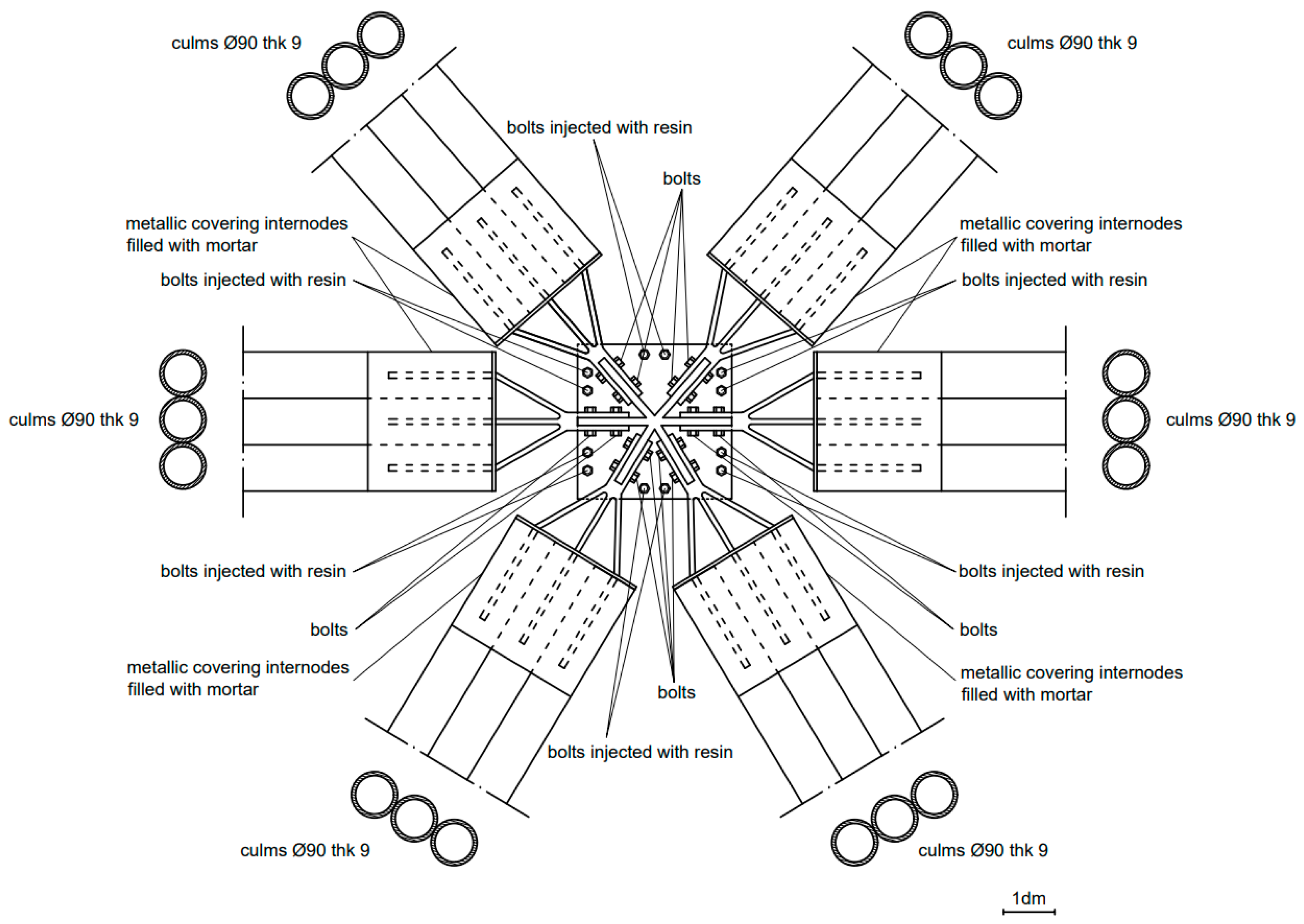
Sustainability Free Full Text Building Retrofitting System Based On Bamboo Steel Hybrid Exoskeleton Structures A Case Study Html

A Rc Column Subjected To Lateral Load Under Seismic Condition B Download Scientific Diagram

Seismic Damage Mitigation Strategy Using An Frp Column Jacketing System In Gravity Designed Reinforced Concrete Building Frames Sciencedirect
Comments
Post a Comment